Leveraging AI and Generative AI for Precision Agriculture: Techniques, Case Studies, and Insights
20/10/2025
Oct 20 , 2025 read
Modern agriculture faces mounting challenges. Climate change disrupts seasonal patterns, labor shortages limit operational capacity, and global food demand continues to rise. Traditional methods of farm management struggle to meet these pressures efficiently.
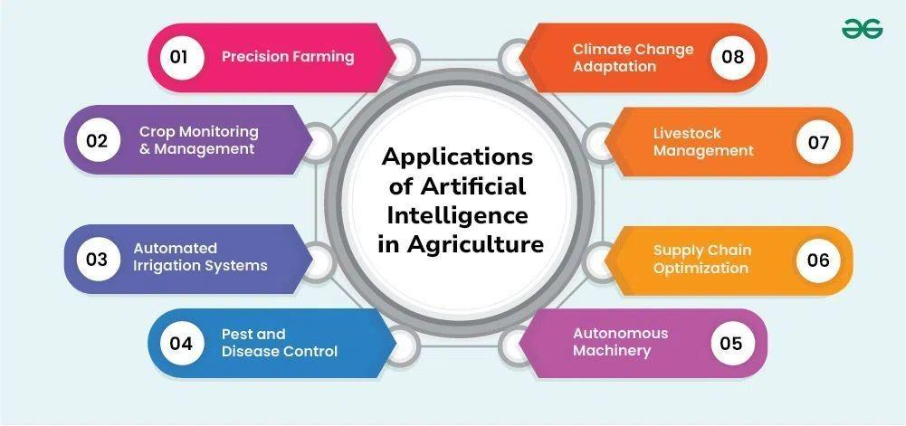
Artificial intelligence (AI) has long been applied to optimize specific tasks such as irrigation, fertilization, and yield prediction. Recent advances in generative AI (Gen AI) now extend these capabilities, enabling cross-domain problem-solving—from predicting crop yields to optimizing supply chains and simulating complex agricultural scenarios.

This article explores how AI and Gen AI are revolutionizing agriculture, highlighting techniques, real-world implementations, and the challenges that lie ahead.
AI for On-Farm Operations
AI’s most immediate impact is on the farm itself, enhancing efficiency, precision, and sustainability across crop and livestock production.

Seed Selection and Crop Planning
Selecting the right seeds and planning crop cycles are critical for maximizing yield and resilience. AI transforms these decisions through:
- Predictive modeling: Machine learning models such as random forests and gradient boosting analyze soil data, weather forecasts, and historical yields to predict germination success with over 85% accuracy.
- Soil and nutrient assessment: Sensors and drones monitor soil health, nutrient levels, and hybrid variety performance. Image recognition tools perform quality checks on seeds.
- Cognitive recommendations: AI systems suggest crops tailored to local climate, soil conditions, and potential pest pressures.
For crop planning, AI integrates climate data, historical trends, and farm-specific characteristics to optimize:
- Sowing schedules and rotations
- Field placement based on soil and topography
- Plant spacing and depth for optimal growth
Example: Drone imagery and geographic analysis can identify micro-zones in a field, allowing precision planting at the level of individual square meters, not just acres.
Impact: By combining real-time monitoring (drones, satellites, IoT devices) with historical data, farmers can make data-driven, adaptive decisions throughout the planting season.
Precision Resource Management
Efficient use of water and nutrients is central to sustainable farming. AI helps by predicting needs with unprecedented precision:
| Resource | AI Application | Benefit |
| Water | Uses sensor networks and evapotranspiration models to schedule irrigation; drone/satellite imagery detects soil moisture variability | Reduces water usage, prevents over-irrigation, lowers labor |
| Fertilizer | Analyzes soil composition and crop history to forecast deficiencies; recommends dosage and timing | Optimizes yield, minimizes environmental impact |
AI-powered irrigation systems automatically adjust water distribution, detect leaks, and maintain ideal soil moisture. Similarly, nutrient management leverages predictive analytics to apply fertilizers only where and when needed, enhancing efficiency and sustainability.
Pest and Disease Detection
AI enables real-time crop health monitoring. High-resolution imagery from drones and satellites is analyzed using computer vision to detect:
- Disease spots and early infections
- Pest infestations (e.g., locusts, grasshoppers)
- Nutrient deficiencies and weed growth
Generative AI adds a proactive layer by simulating pest outbreaks and environmental stresses, helping farmers anticipate problems and plan interventions.
Key advantage: AI can recommend targeted herbicide or pesticide application, adjusting doses to current infestation levels instead of relying on fixed schedules. Gen AI can also synthesize vast datasets to propose optimized crop protection strategies, effectively serving as a virtual agronomist.
Yield Prediction and Crop Health Monitoring
AI improves yield forecasting and crop management by integrating multiple data sources:
- Sensors: Soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels
- Imaging technologies: Hyperspectral imaging, 3D laser scanning, and infrared cameras
- Satellite/drone data: High-resolution crop and soil monitoring
Benefits:
- Early detection of stress, disease, or pest infestation
- Optimized fertilization and irrigation
- Accurate yield predictions to guide sowing, harvesting, and pricing
For instance, vegetation indices like NDVI derived from multispectral imagery allow AI to detect subtle deviations in crop performance, enabling proactive intervention before visible damage occurs.
Automation and Robotics
Labor shortages are a growing concern in agriculture. AI-driven automation addresses this by enhancing precision, efficiency, and productivity:
| Technology | Application | Benefit |
| Autonomous tractors | GPS-guided field operations, tilling, planting, harvesting | High precision at plant-level scale, reduces errors, optimizes resource use |
| Drones | Targeted pesticide/herbicide application, monitoring weed infestations | Reduces chemical use, increases efficiency, lowers labor |
| Harvesting robots | Sorting, packing, harvesting crops | Improves speed, accuracy, and crop quality |
By combining these tools, farms can perform tasks more reliably and sustainably than ever before, reducing waste and maximizing output.
AI for Enterprise Operations
Beyond the farm, AI and Gen AI optimize research, supply chains, and business operations.
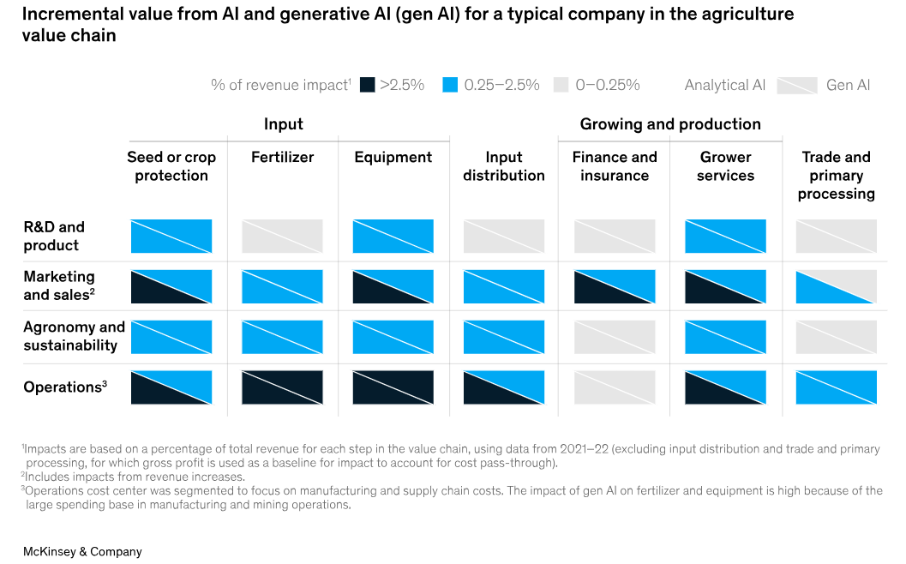
Research & Development (R&D)
Gen AI accelerates agricultural innovation by:
- Hypothesis generation: Scans scientific literature, patents, and genomic datasets to propose novel crop traits, such as drought or pest resistance.
- Prioritization: Models recommend experiments with the highest likelihood of success, creating an active learning loop where results refine predictions.
- Automation: Generates regulatory documents, compliance reports, and other workflow tasks to reduce time-to-market.
This integration streamlines the full R&D lifecycle, enabling faster, data-driven innovation.
Supply Chain & Operational Efficiency
AI transforms supply chains by predicting disruptions, optimizing inventory, and improving operational planning:
- Scenario simulations: Gen AI models weather, trade, and environmental changes to propose SKU-level adjustments.
- Predictive maintenance: AI analyzes sensor data (e.g., soil, feed, equipment performance) to anticipate failures and optimize scheduling.
Impact: Farms and agribusinesses can maintain consistent product quality, reduce downtime, and enhance operational reliability.
Marketing, Sales, and Finance
AI supports strategic decisions through:
- Demand forecasting: Predicts sales trends, pricing fluctuations, and market dynamics
- Personalized marketing: Gen AI generates content and sales scripts tailored to customer profiles
- Financial analysis: Assesses farmer creditworthiness using operational and yield data, reducing lending risk
By providing actionable insights across the value chain, AI fosters financial stability and strategic growth in agriculture.
Case Study: Wheat Farming in the U.S. Midwest
Problem: Variable rainfall creates uncertainty in wheat yield, impacting planting and fertilization decisions.
Method: An ensemble ML model combined satellite imagery, IoT soil sensors, and historical climate data:
- Satellite imagery: Multispectral photos identify nutrient deficiencies, disease spots, and stress
- IoT sensors: Continuous soil monitoring informs irrigation and fertilizer application
- Historical climate data: Decades of records improve predictive accuracy
Results:
- Yield prediction accuracy: R² = 0.87
- Fertilizer and water usage reduced by 12% without quality compromise
Next Steps: Integrating Gen AI can simulate pest outbreaks and complex environmental scenarios, acting as a virtual agronomy adviser for proactive decision-making.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promise of AI, several hurdles remain:
- Data quality and availability: High-resolution, multi-source datasets are essential
- Farmer digital literacy: Adoption depends on intuitive interfaces
- Infrastructure limitations: Edge computing, 5G connectivity, and IoT deployment are critical
- Ethics and sustainability: AI systems must minimize environmental impact and avoid biases
Future research will likely focus on cross-domain AI systems, combining on-farm monitoring, predictive modeling, and enterprise-level optimization for truly intelligent agriculture.
Conclusion
AI and generative AI are transforming agriculture from the ground up. By integrating predictive analytics, generative simulations, and automation, farms can:
- Optimize resource use
- Increase yields
- Reduce environmental impact
- Enhance operational efficiency
The combination of analytical AI and Gen AI enables farmers and agribusinesses to make smarter, faster, and more sustainable decisions, creating a resilient and productive agricultural ecosystem for the future.
Further readings
- From bytes to bushels: How gen AI can shape the future of agriculture: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/agriculture/our-insights/from-bytes-to-bushels-how-gen-ai-can-shape-the-future-of-agriculture
- Understanding the potential applications of Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture Sector: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S277323712200020X